🚀 LightRAG
Simple and Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Why did I choose this paper?
- One of our core areas of focus is natural products. Our objective is to extract, curate, and derive insights from natural product (NP) data published across journals, literature, and web articles spanning decades, while also leveraging knowledge from newly published works.
- We aim to extract and process this information in a cost-effective manner, with the ultimate aim of achieving higher level of factual accuracy and abstract understanding of NP chemistry.
- While retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) represents a recent and promising architecture for this purpose, it has inherent limitations. Upon further exploration, LightRAG has emerged as a more effective solution, addressing many of our requirements more comprehensively compared to fine-tuning traditional LLMs.
Introduction
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems enhance large language models (LLMs) byintegrating external knowledge sources, enabling more accurate and contextuallyrelevant responses tailored to user needs. However, existing RAG systems havesignificant limitations, including reliance on flat data representations andinadequate contextual awareness, which can lead to fragmented answers that fail tocapture complex inter-dependencies. To address these challenges, we propose LightRAG,which incorporates graph structures into text indexing and retrieval processes. Thisinnovative framework employs a dual-level retrieval system that enhances comprehensiveinformation retrieval from both low-level and high-level knowledge discovery. Additionally,the integration of graph structures with vector representations facilitates efficientretrieval of related entities and their relationships, significantly improving responsetimes while maintaining contextual relevance. This capability is further enhanced by anincremental update algorithm that ensures the timely integration of new data, allowing thesystem to remain effective and responsive in rapidly changing data environments. Extensiveexperimental validation demonstrates considerable improvements in retrieval accuracy andefficiency compared to existing approaches.
Technical Description
Architecture
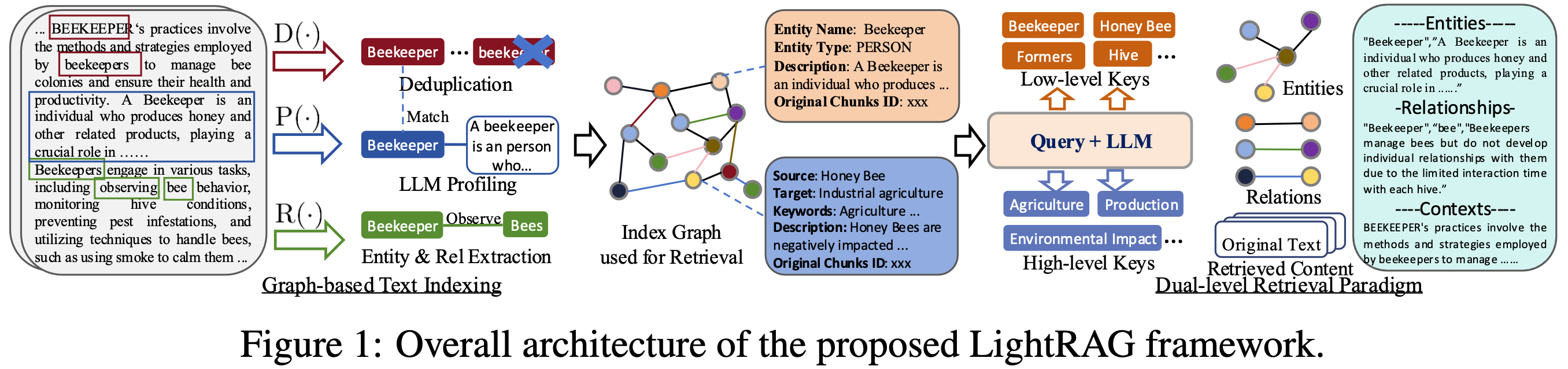
Graph-Enhanced Entity and Relationship Extraction
LightRAG enhances the retrieval system by segmenting documents into smaller, more manageable pieces. This strategy allows for quick identification and access to relevant information without analyzing entire documents. The process includes the following functions:Extracting Entities and Relationships (R):
Prompts an LLM to identify entities (nodes) and their relationships (edges) within the text data. For example, entities like “Cardiologists” and “Heart Disease” and relationships such as “Cardiologists diagnose Heart Disease” can be extracted. Raw text is segmented into multiple chunks for efficiency.LLM Profiling for Key-Value Pair Generation (P):
Uses a profiling function to generate key-value pairs for each entity and relation. Keys are words or short phrases for retrieval, while values summarize relevant snippets for text generation.Deduplication to Optimize Graph Operations (D):
Merges identical entities and relations from different text segments, reducing graph size and improving processing efficiency.
Advantages:
- Comprehensive Information Understanding: Graph structures enable multi-hop subgraph extraction for complex queries.
- Enhanced Retrieval Performance: Key-value structures optimize retrieval accuracy and efficiency.
Fast Adaptation to Incremental Knowledge Base
LightRAG adapts efficiently to evolving data by incrementally updating the knowledge base without reprocessing the entire database.- Seamless Integration of New Data: Consistently integrates new data while preserving existing graph integrity.
- Reducing Computational Overhead: Eliminates the need to rebuild the entire graph, conserving resources and maintaining system accuracy.
Dual-level Retrieval Paradigm
Supports detailed and abstract queries for specific and broader information retrieval.- Specific Queries: Target precise details (e.g., “Who wrote ‘Pride and Prejudice’?”).
- Abstract Queries: Cover broader topics (e.g., “How does AI influence modern education?”).
Combines low-level and high-level retrieval strategies for effective query handling.
Retrieval-Augmented Answer Generation
Uses an LLM to generate answers by unifying the query with multi-source data, ensuring relevance and alignment with user needs.
Algorithm Flowchart
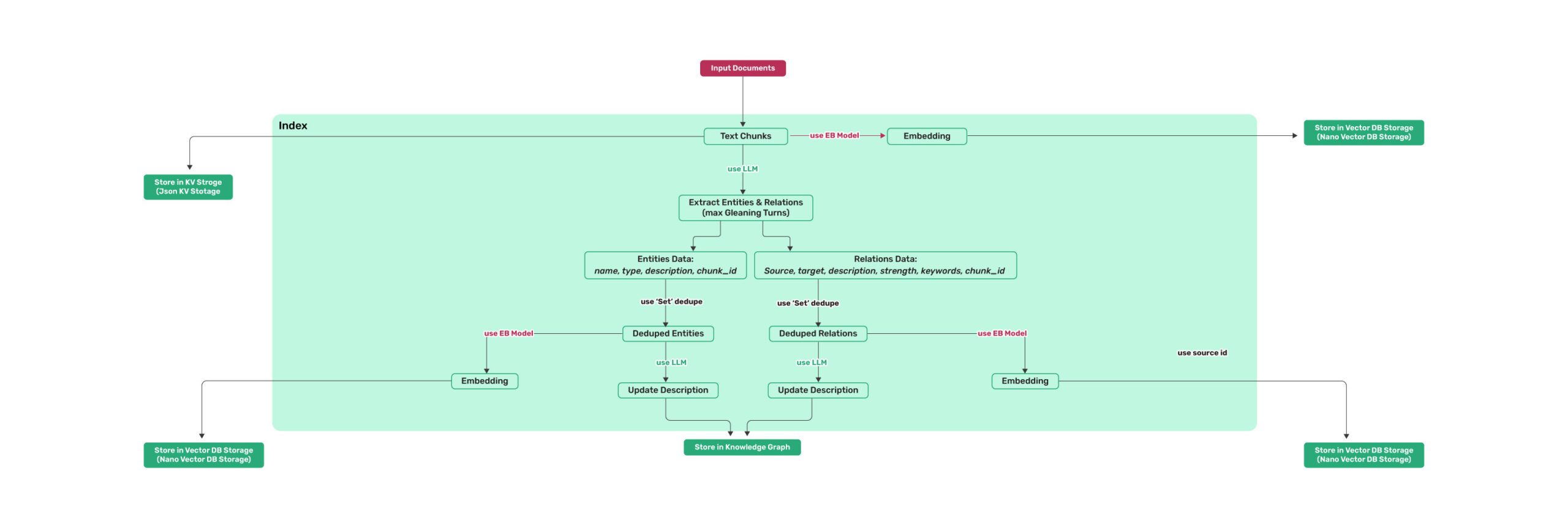 Figure 1: LightRAG Indexing Flowchart - Img Caption : Source
Figure 1: LightRAG Indexing Flowchart - Img Caption : Source 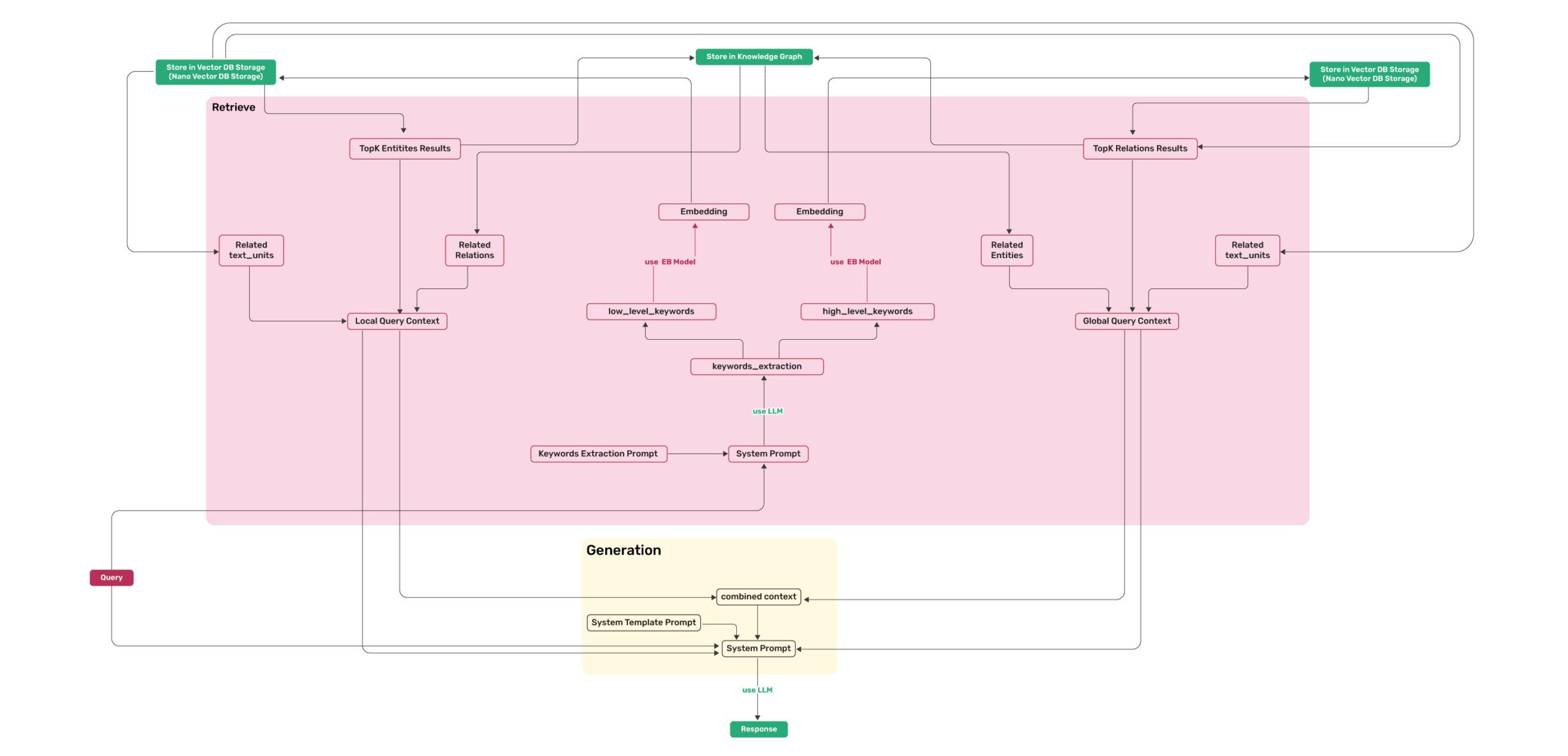 Figure 2: LightRAG Retrieval and Querying Flowchart - Img Caption : Source
Figure 2: LightRAG Retrieval and Querying Flowchart - Img Caption : Source
Experiments
Defining ground truth for complex RAG queries is challenging. To address this, LightRAG adopts an LLM-based multi-dimensional comparison method, using GPT-4o-mini for evaluation across four dimensions:
- Comprehensiveness: How thoroughly the answer addresses all aspects of the question.
- Diversity: The richness of perspectives and insights.
- Empowerment: How effectively the answer enables understanding and informed judgments.
- Overall: The cumulative performance across all dimensions.
Comparison with Existing RAG Methods
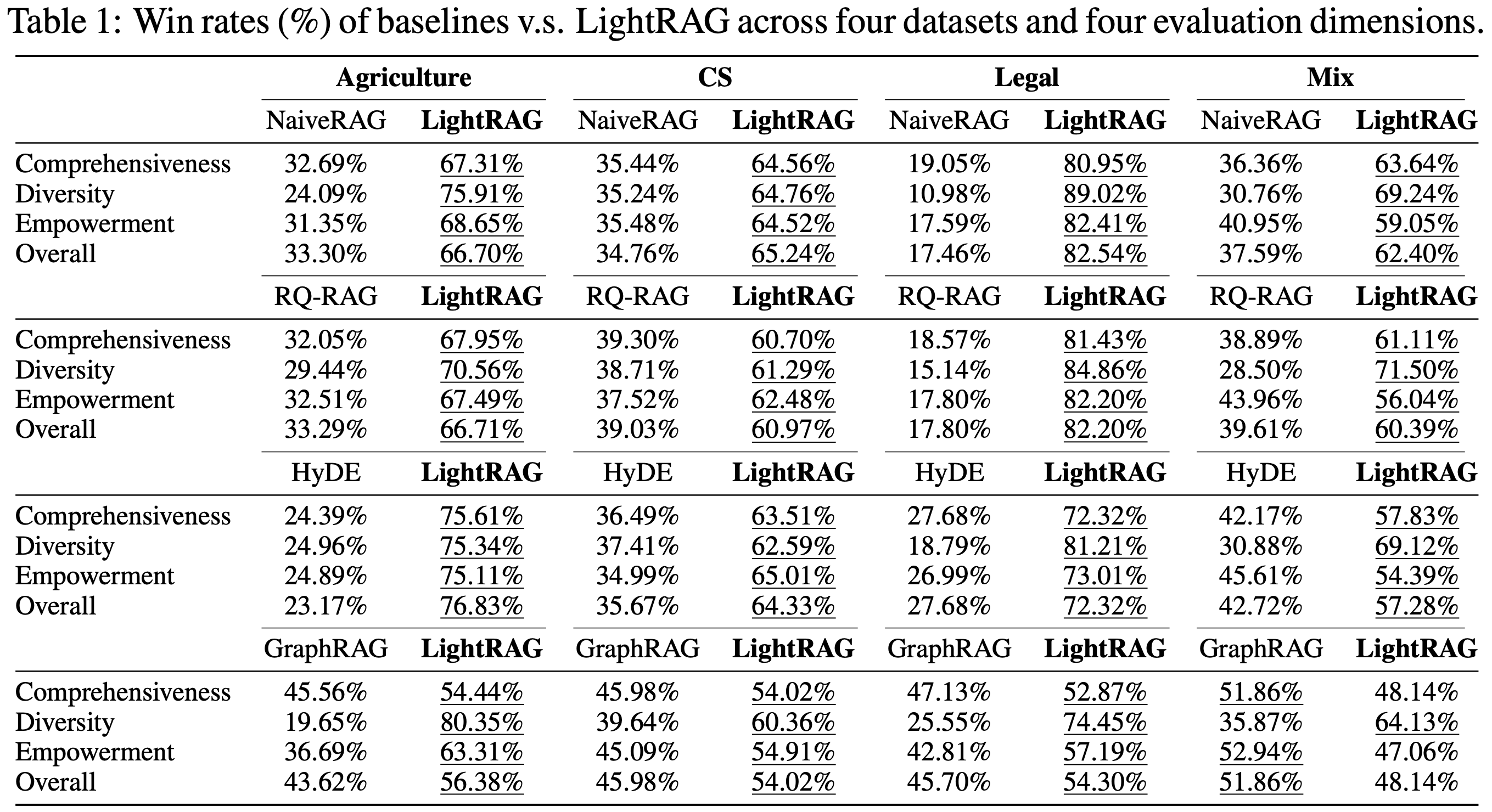
LightRAG outperforms baselines across evaluation dimensions and datasets. Results are shown in Table 1:
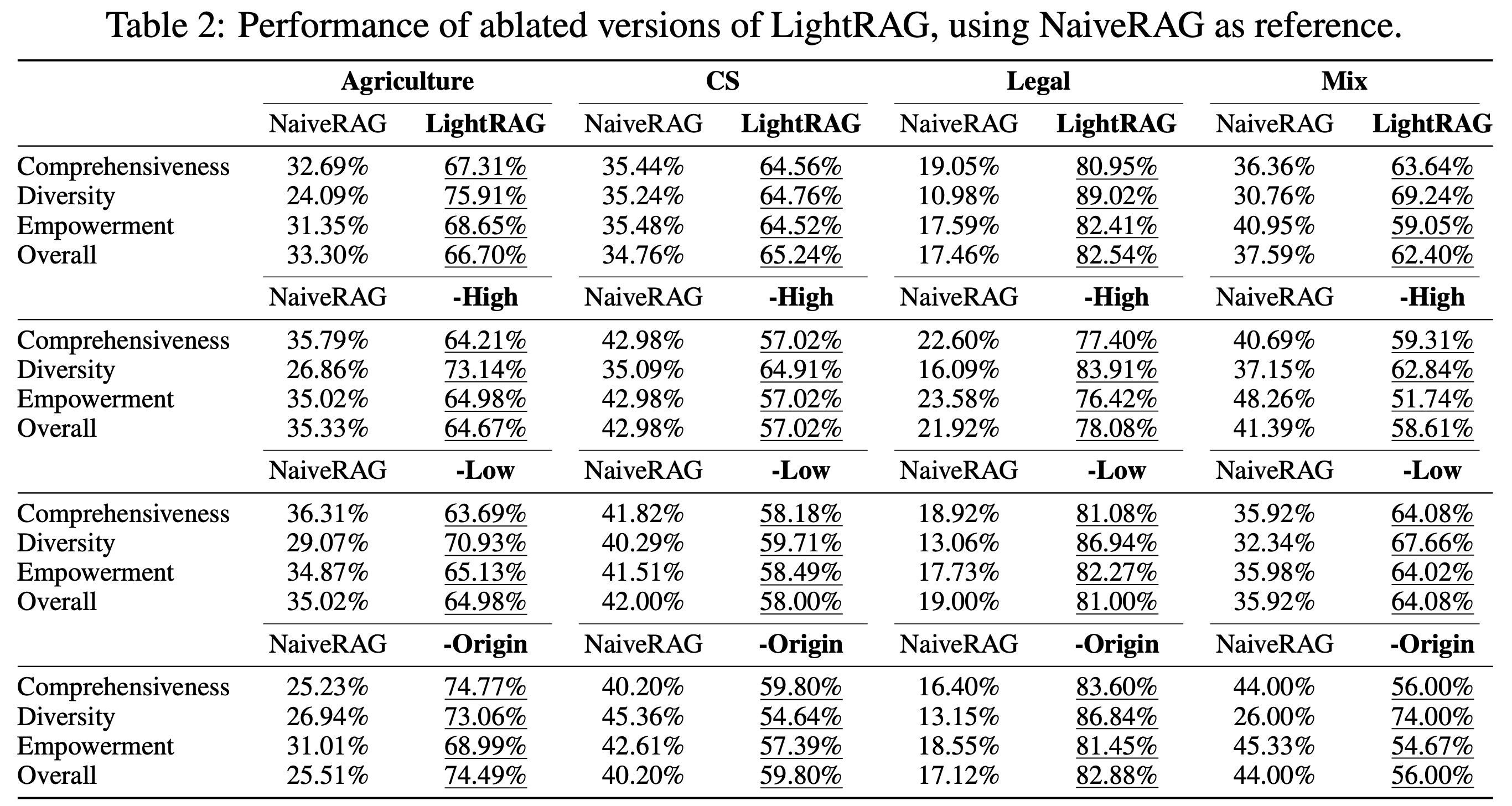
Ablation Study
Analyzed the impact of low-level and high-level retrieval paradigms:
- Low-level-only Retrieval: Focuses on specific entities but struggles with complex queries.
- High-level-only Retrieval: Gathers broad content but lacks detailed insights.
- Hybrid Mode: Combines both approaches, ensuring comprehensive and detailed data retrieval.
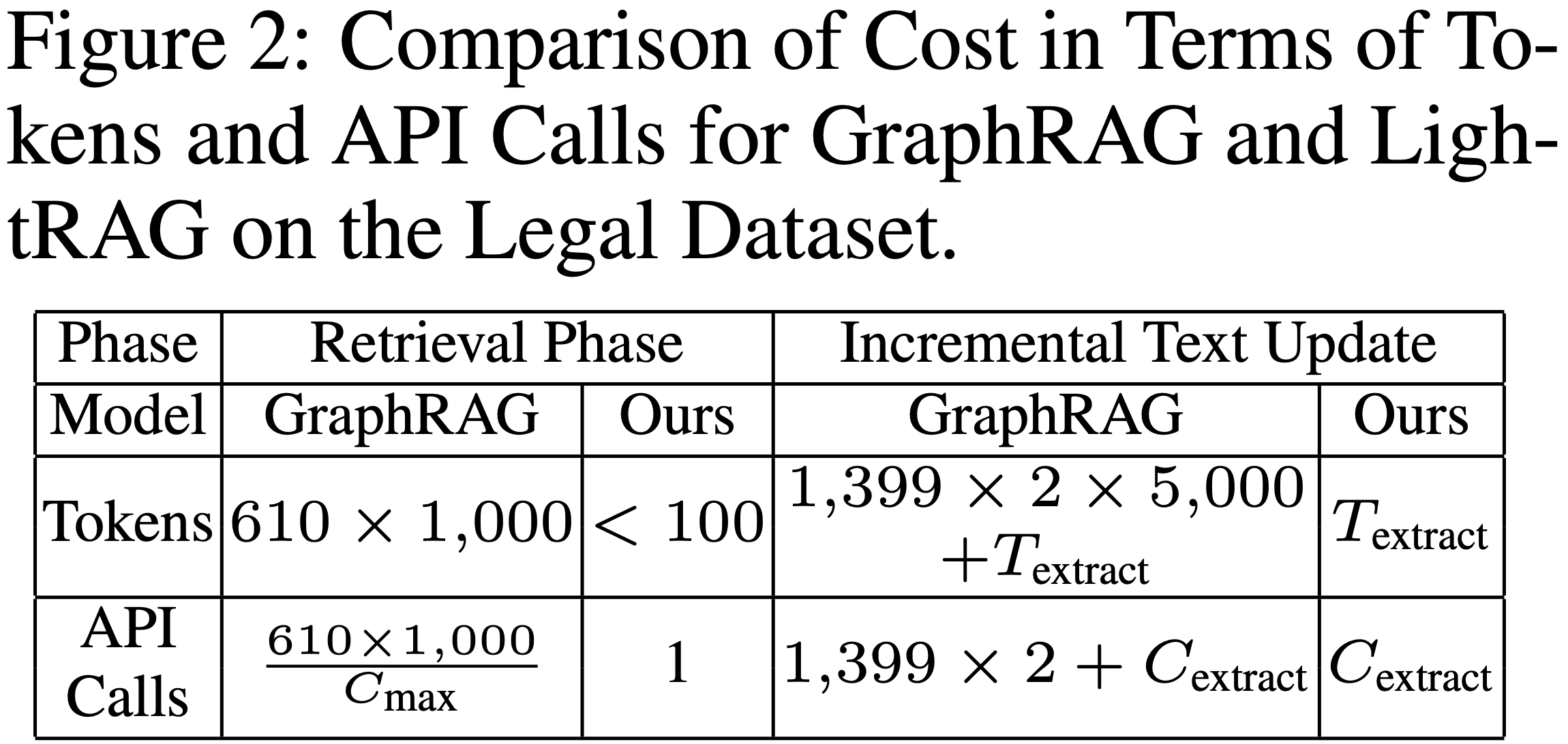
Model Cost and Adaptability Analysis
Compared LightRAG with GraphRAG in terms of tokens, API calls, and adaptability to dynamic data changes. Results are shown in Table:
Conclusion
This work presents a significant advancement in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) by integrating a graph-based indexing approach that enhances both the efficiency and depth of information retrieval. LightRAG employs a comprehensive knowledge graph to enable rapid and relevant document retrieval, facilitating a more profound understanding of complex queries. Its dual-level retrieval paradigm supports the extraction of both specific details and abstract insights, addressing diverse user requirements. Additionally, LightRAG’s seamless incremental update mechanism ensures the system remains adaptive and effective, maintaining its relevance in the face of evolving data. By excelling in efficiency and effectiveness, LightRAG substantially improves the speed and quality of information retrieval and generation while reducing the costs associated with LLM inference.
Only time will reveal the true potential of the LightRAG architecture as an effective tool for extracting natural product (NP) data / metadata in a structured format, and ultimately submitting it to COCONUT to support broader research initiatives and further curation efforts in the field.
